tibial compression test dog|cranial cruciate rupture canine : factories A positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm CCLR. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect . Alemanha. 0-0-0. Acesse ESPN (BR) para resultados ao vivo, vídeos e notícias do Alemanha. Encontre a classificação e o cronograma completo da temporada de 2024.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBThe latest tweets from @OCasalBrSw
By Phil Zeltzman, DVM. This very useful test can be performed with the patient standing or in lateral recumbency (affected leg up), awake or sedated. The stifle is held in slight flexion. The index finger of one hand is placed over the tibial crest. The other hand flexes & .
Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early CrCLD. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable .
The tibial compression test (TCT) is a very useful diagnostic tool for identifying a torn Cranial Cruciate ligament in the dog.
A positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm CCLR. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect .
Figure 5B A dog undergoing a tibial compression test. Examine the unaffected pelvic limb first to establish a baseline, and palpate from the digits toward the pelvis. Examine the upper-most limb of the laterally recumbent .
A video demonstrating how to perform a tibial compression test (or tibial thrust test) in the canine patient.A tibial compression test (flexion of the hock and cranial displacement of the tibial tuberosity) can also be used to demonstrate laxity of the cranial cruciate ligament. Radiography reveals joint effusion and signs of degenerative joint disease in .DIAGNOSIS. In early partial rupture joint palpation is still normal and no swelling is felt on the caudomedial joint compartment were a separation between the femoral condyle and the tibial .•Tibial compression test performed with axial loading and full stifle range of motion •Sensitivity 63% vs 40-50% using conventional exam techniques •Specificity 77%
There are several tests your veterinarian can perform to check for this abnormality, with some of the most common being the cranial drawer test and the tibial compression test. .Objective: To assess diagnostic efficacy of a modified tibial compression test in predicting medial meniscal injury in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament failure. Methods: Dogs admitted for surgical stabilisation of stifles with cranial cruciate ligament failure were examined by five preoperative physical tests to assess medial meniscal injury. The beauty of the tibial compression test is that it mimics the loading that causes cranial tibial thrust when the dog walks. This is very different than the cranial drawer sign, which is a motion that doesn’t exist in real life. Think of it this way: The cranial drawer sign is “iatrogenic” whereas the cranial tibial thrust is generated .
It is important to support the dog with the other hand while doing the test as most dog will sit as soon as you apply pressure. Lumbo-sacral pain can also be detected with the “tail jack” test. The tail is lifted until you encounter resistance. . “Tibial compression test”: The leg is held in a normal weight bearing position. One hand .This video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust) tests. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative.The tibial compression test has the advantage that it can be done in the standing animal, which is especially helpful in large dogs. The disadvantage is that for many examiners, a positive tibial compression test is not detected as consistently as a cranial drawer sign . The ability to rotate the tibia medially with respect to the femur to a .Most dogs will tolerate a comprehensive orthopaedic examination without the use of sedation, although some tests, such as cranial drawer and tibial compression test, may be more sensitive when performed under sedation. 1. The key to a successful orthopaedic examination is to be methodical and thorough. Start with the dog standing and facing .
Henderson R A, Milton J L (1978) The tibial compression mechanism - a diagnostic aid in stifle injuries. JAAHA 14 (4), 474-479 VetMedResource . Go back
Shrinkage Testing advice
A cranial draw sign was present in all dogs; the tibial compression test was positive in 51 cases (79.6%). Seven post-operative complications were encountered (11%). There were two fractures through the tibial tuberosity, one joint infection, one plate infection, one case of suspect bone neoplasia, and two meniscal injuries.
Objective: To determine the sensitivity and specificity of the drawer test (DT) alone and in combination with the tibial compression test (TCT) to detect stifle subluxation after transection of the cranial cruciate (CrCL), caudal cruciate (CdCL) or both cruciate ligaments (total cruciate ligament or TCL). Study design: Experimental study.I really like the tibial compression test (TCT), or tibial thrust, as a diagnostic tool for dogs with a damaged cranial cruciate ligament. I have small hands and sometimes doing a drawer test on a large dog is almost impossible because I cannot properly position my .
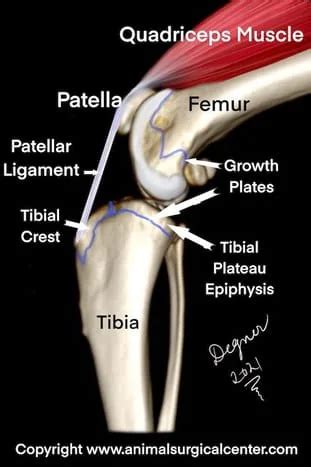
tibial crest on a dog
The tibial compression test—cranial tibial thrust—is useful because it mimics what happens in the knee when the dog walks. If there is CCL damage, the bone moves forward when the hock is in the flexed position. . Diagnosis of Cranial Cruciate LigamentIinjury in Dogs by Tibial Compression Radiography. The drawer sign. A drawer sign, or .Tibial Compression Test: Another test that is used to diagnose dog ACL injuries is the tibial compression test. In this assessment, one hand is placed around the end of the femur, with the index finger extended over the patella. The other hand grasps the foot and flexes the hock (ankle). If the tibia moves forward, it is an indication of ACL .However, it has been found that the drawer test, when performed in isolation or combined with the tibial compression test “poorly differentiates” the cause of stifle instability. It is not possible to palpate instability at the stifle joint of dogs with chronic CrCLR because of .
Cranial tibial thrust is the stifle vector force created by the dog when weight-bearing, which results in cranial translation of the tibia with each step in a dog with CrCLR. The correct performance of either test is a learned skill, mastered only after much experience and practice on healthy dogs as well as those with partial or complete CrCLRs. Objectives. To investigate the accuracy and intra- and interobserver reliability of the cranial drawer test (CD), tibial compression test (TCT), and the new tibial pivot compression test (TPCT) in an experimental setting resembling acute cranial cruciate ligament rupture (CCLR) and to elucidate the ability to subjectively estimate cranial tibial translation (CTT) during testing.Physical examination tests that are helpful in diagnosing a partial CrCL tear include the sit test, stifle hyperextension test, cranial drawer test, and the tibial compression test. A positive sit test is observed when the affected hind leg is positioned in a .forms was used in each dog to objectively quantify the in vivo cranial tibial translation, keeping 135˚ of joint angle, which is typically considered as the average standing angle of the canine sti-fle [21–23] and as performed by Lopez and collaborators [9]. Dogs under general anaesthesia were positioned in lateral recumbence with the hind limb
A cranial drawer test or tibial compression test is used to evaluate craniocaudal instability of the stifle joint [7]. Recently, it was determined that the drawer test alone or combined with the . Unfortunately, some dogs may still exhibit an abnormal sit test following CCL stabilization. The reason for this is unknown but it could be due to continued stifle discomfort upon full flexion. . Instability of the stifle is commonly demonstrated through the cranial drawer test and tibial compression test. The cranial drawer test is performed . In dogs, CCL rupture is most commonly diagnosed by means of specific orthopedic tests, such as the drawer test and the tibial compression (TC) test, both of which assess joint stability and promote cranial tibial translation in relation to the femur if ligament insufficiency or rupture is present. 5 Complementary imaging-based tests may prove .
In these dogs the cranial tibial thrust caused by the forces acting on the slope of the tibial plateau continuously stresses the CrCL and causes its partial rupture progressing with time in complete rupture. . The tibial compression test (TCT) is negative as it is the drawer sign. Early ligament sprains are suspected radiographically in the . The sensitivity of the radiographic tibial compression test was 97 per cent, compared with 86 per cent for the cranial drawer test; the specificities of the tests were 100 per cent and nearly 98 . To assess diagnostic efficacy of a modified tibial compression test in predicting medial meniscal injury in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament failure. Methods Dogs admitted for surgical stabilisation of stifles with cranial cruciate ligament failure were examined by five preoperative physical tests to assess medial meniscal injury.
Detection and estimation of severity of cranial tibial translation enable the diagnosis of CR and also the inference of the severity of CrCL fibre rupture, particularly with the tibial compression test in extension. Severity of joint laxity is best assessed .Tibial compression test Tibia: compression test. Requirements. Subscribe To View This article is available to subscribers. . On the veterinary diagnosis and treatment of your choice of species: dogs, cats, rabbits, exotics, horses and cattle. Starting at: £40 /month. View Pricing Options Extend My Trial. An audible "clicking" may be heard when the stifle is taken through its range of motion when a meniscal tear is present. Positive cranial drawer and cranial tibial thrust during a tibial compression test are definitive tests for cruciate instability. To check for cranial drawer, the dog is placed in lateral recumbency with the affected limb up.
Objective: To assess diagnostic efficacy of a modified tibial compression test in predicting medial meniscal injury in dogs with cranial cruciate ligament failure.
ruptured cruciate ligament dog
positive cranial drawer dog
webTransar é preciso. Faz bem para a pele, aumenta imunidade, relaxa.siga para saber mais e tudo sobre desejo e orgasmo feminino 50+. "O clitóris é um organismo bastante .
tibial compression test dog|cranial cruciate rupture canine